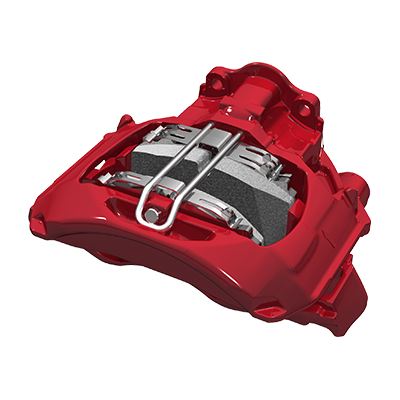
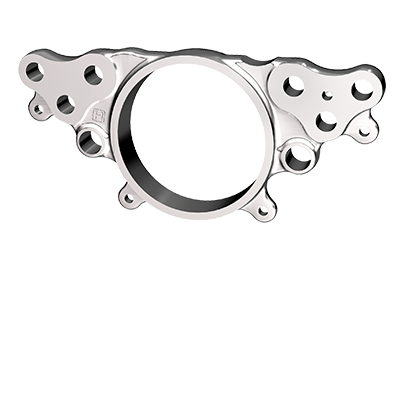
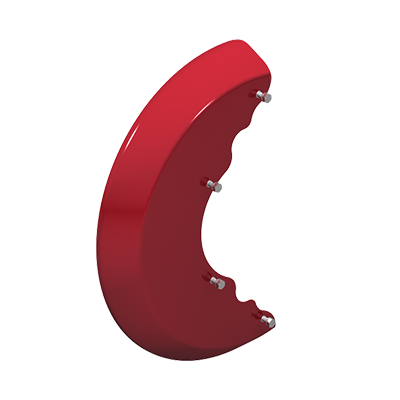
- Learn the location of the identification (ID) tag.
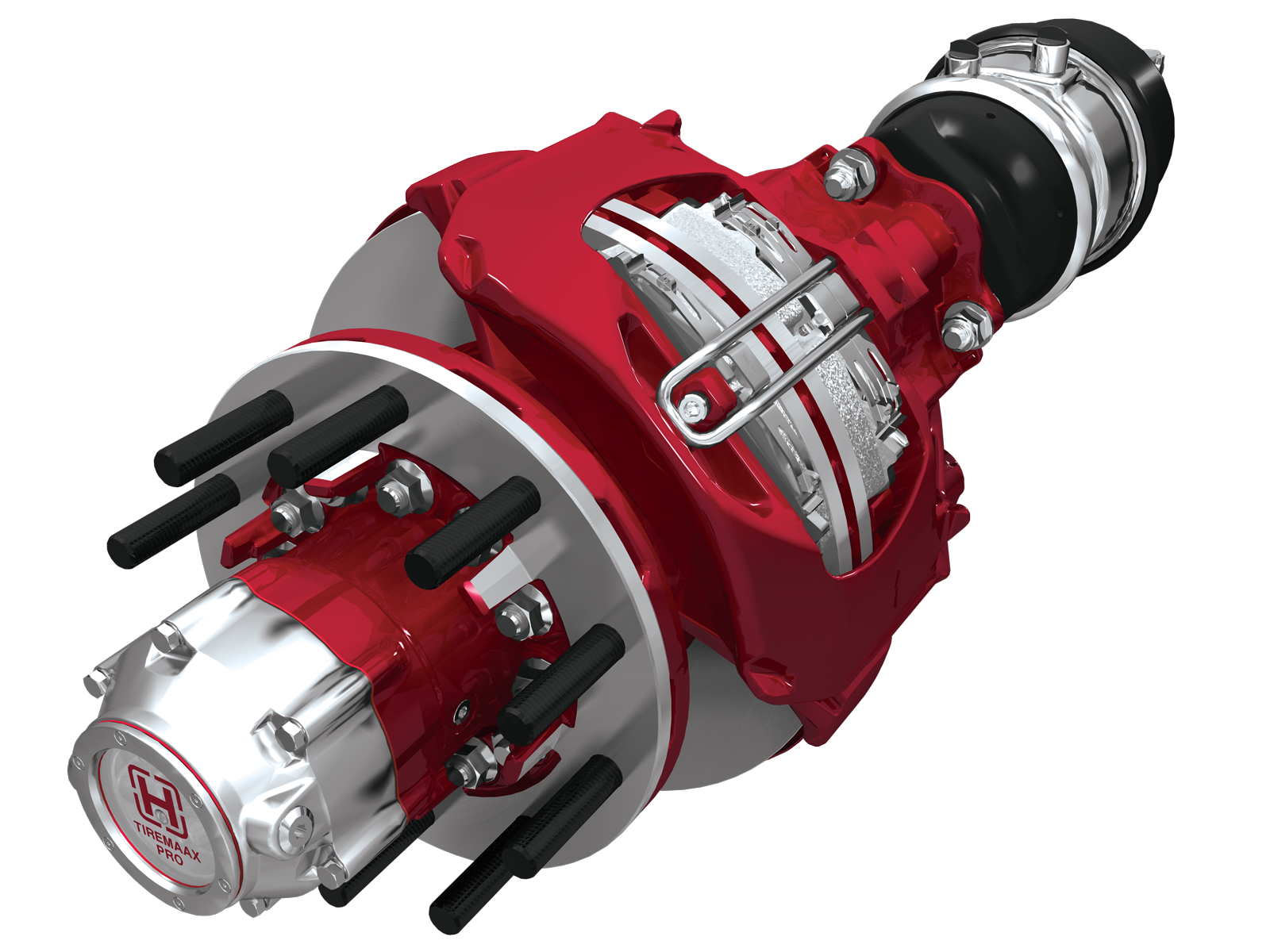
The ID tag often includes the brand and model of the air disc brake system. Typically, ID tags are located on the inboard side of the caliper /carrier assembly or on the guide pin.
L1063 - ADB Parts List - Identify visual differences between air disc brake brands.
If the ID tag is missing, other visual cues can help identify the system. Pay attention to key components like the spreader plate, the retaining bar and the screws that hold the bar in place. Some systems use a spreader plate while others do not. Some also use a flat retaining bar versus a tubular retaining bar. Furthermore, the type of screw that is used to hold the retaining bar in place varies between air disc brake systems.
L949 - READY-TO-ROLL Wheel-End Catalog
L1063 - AIR DISC BRAKES PARTS LIST
- Keep helpful tools at your fingertips.
Have a good set of up-to-date reference tools handy to make identifying, stocking and replacing components quick and convenient. Recommended stocking lists, part number cross reference lists, parts lists and maintenance manuals can go a long way to saving time and frustration at the beginning of the service process.
L949 - READY-TO-ROLL Wheel-End Catalog
L1063 - AIR DISC BRAKES PARTS LIST
L1000 - WAREHOUSE RECOMMENDED STOCKING LIST
L1181 - DEALER RECOMMENDED STOCKING LIST
L1332 - COPPER-FREE BRAKE INITIATIVE
PLUS+ PARTS LOOK-UP SYSTEM
 Optimized Trailer Air Disc Brakes
Optimized Trailer Air Disc Brakes